Substations are essential components of the electrical grid and without them, we wouldn’t be able to ensure stable, safe power for daily use. They play a key role in transmitting high-voltage electricity over long distances and then distributing it at lower voltages to homes, factories, etc.
Designing a substation involves multiple engineering disciplines (like electrical, civil, structural and control engineering) where all areas must work in harmony to ensure the substation operates safely and efficiently.
Modern substations must adhere to several critical standards that protect people from electrical hazards and ensure a consistent power supply. A well-designed substation should:
- Minimize operational risks
- Reduce downtime
- Support new equipment technologies
This article explores what substation design entails, the key aspects and components involved, and the engineering considerations necessary to build efficient and resilient electrical infrastructure.
What Does Substation Design Entail?
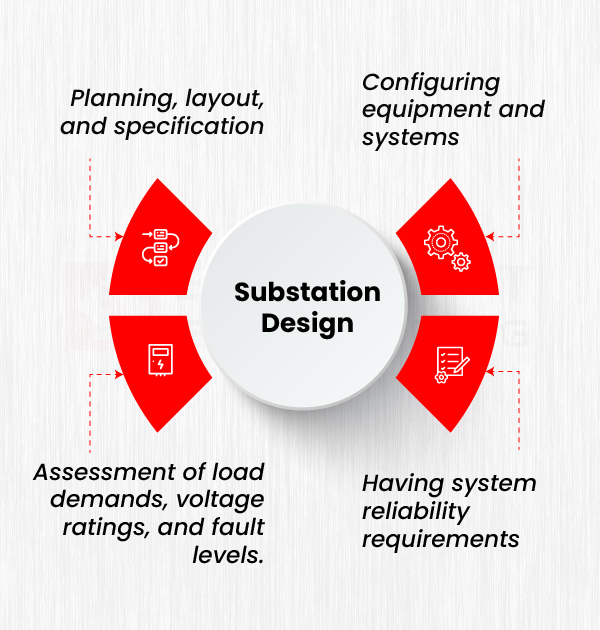
Substation design is the process of creating a blueprint or plan for a facility where electricity is managed. Designing a substation is multifaceted engineering process which typically involves:
- Planning, layout, and specification which includes deciding what equipment is needed, where it will be placed, and how it will be connected.
- Configuring equipment and systems like transformers, circuit breakers, switchgear and relays. Designers must carefully select the right types and sizes of equipment to handle the power load and ensure safe operation.
- Assessment of load demands, voltage ratings, and fault levels. Factoring these in the design makes sure the substation can handle the appropriate voltage, and there are protective measures in place.
- Having system reliability requirements, which are the design targets and standards, to ensure the substation keeps power flowing without interruptions, even during failures or maintenance.
A substation design service provider prioritize safety, compliance, and environmental protection along with functionality.
Key Aspects of Substation Design
Designing a substation requires evaluating several factors that can affect and ensure proper function of the facility. Here are some of the key aspects that should invariably be included while designing a robust substation.
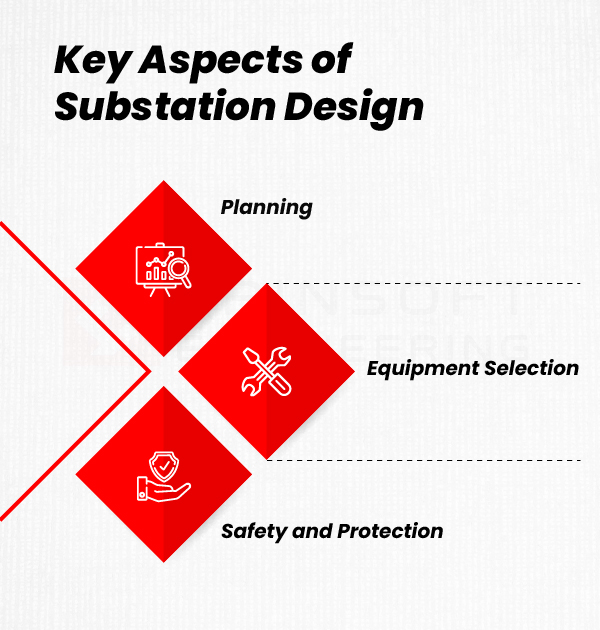
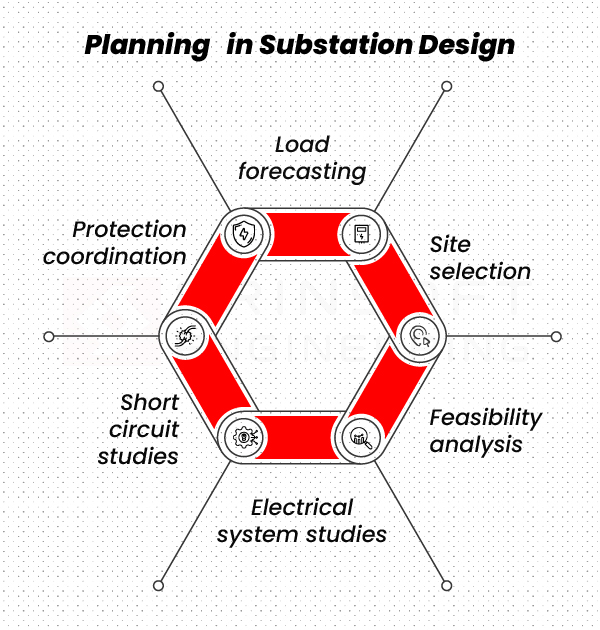
1. Planning
The initial stage of substation design involves detailed analysis of the following
- Load forecasting: This involves predicting how much electricity the area will need both now and in the future.
- Site selection: Choosing the best physical location for the substation.
- Feasibility analysis: Engineers evaluate whether building a substation at a particular site is technically and economically practical.
- Electrical system studies: These are simulations or analyses that predict how the power system will behave under various conditions.
- Short circuit studies: Engineers calculate the maximum current that could flow during a fault (like a short circuit), so they can choose equipment that can safely handle it.
- Protection coordination: This ensures that protective devices (like relays and circuit breakers) work together properly when something goes wrong.
2. Equipment Selection
Substations rely on multiple electrical devices to function safely and efficiently. Selecting the correct type of equipment is crucial because it directly affects system performance, safety, and reliability.
Some of the critical equipment that needs to be chosen while designing includes transformers, circuit breakers, relays, grounding systems and disconnect switches.
Over and above choosing the right equipment, each one must be chosen based on technical needs like voltage, current, protection, and future growth, to ensure safe and efficient operation.
3. Safety and Protection
Having built-in safety features protect both people and equipment in a substation. Some of the effective safety components that a design must include are grounding, surge protection, arc-flash mitigation, and personnel clearances.
Also, having automated protection systems that respond instantly to faults ensures the rest of the system stays operational. Having protections schemes in the design like relays, and smart automations (like SCADA) help isolate the faults and prevent widespread blackouts or equipment loss.
Core Components in Substation Design
Substation design has indispensable elements that contribute to the facility’s reliability and robustness. It is important to optimize them during the design phase so that the substation meets the electrical requirements for efficient functioning. Here are those core components of substation design.
1. Load Calculations and Voltage Levels
Calculating the amount of electrical power the substation will handle (load) and defining the necessary voltage transformation levels helps in accurate selection of transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, and other equipment. It also helps determine whether the substation operates at transmission (132kV and above) or distribution (typically 11kV to 33kV) levels.
Also, correct load and voltage planning prevents overloading (which causes overheating and failure), under sizing (which limits future expansion), and inefficiency in power delivery.
2. Safety Standards
Designers follow international and national codes like IEEE, IEC, and NEC which are essential guidelines for:
- Safe design and installation of electrical systems
- Fault detection and protection measures
- Fire safety and arc-flash mitigation
Adhering to these standards ensures that the design is robust, there is utmost safety for the personnel and public in addition to compliance with local and international laws which are important for project approvals and operations.
3. Layout Planning and Equipment Spacing
Strategically arranging components of a substation (like transformers, switchgear, control panels, etc.) is of paramount importance. Properly designed layouts enable safe working and maintenance zones as well as proper cooling and heat dissipation.
It also helps when the facility needs to be expanded or retrofit components without major changes to the physical structure of the substation.
4. Grounding and Earthing Systems
These are essentially interconnected systems of electrical conductors (like grids, rods, meshes) that route excessive current, produced due to faults or lightning, safely into the earth.
Apart from protecting personnel working in the substations, these systems help keep equipment safe when there is a sudden surge in voltage. Without effective grounding, electronic systems may end up malfunctioning when faults occur.
5. SCADA and Automation Integration
Substations today are no longer entirely manual and rely on automation technologies to handle operations like monitoring, controlling, and protecting the electrical system.
One of the most important pieces of automation technology that substations use is SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), which is a system used to monitor and control processes remotely in real time.
Conclusion
Substation design is about carefully planning the setup that allows electricity to travel efficiently and safely from its source to where it’s needed. Before designing, engineers analyze many factors to ensure the substation is safe, efficient, and meets future needs.
SrinSoft offers end-to-end substation design services with seamless project execution, tailored designs, and compliance with industry standards. Our deep industry knowledge, commitment to safety, and design accuracy make us the preferred choice for engineering high-performance electrical infrastructure. Partner with SrinSoft for reliable and standards-driven substation design.


