You don’t invest to become irrelevant, do you?
That’s why every choice matters, right down to the materials behind your piping infrastructure. Choosing the wrong materials is like building a skyscraper on a cracked foundation: The higher you go, the harder you fall. For leaders, material decisions may seem like plumbing details, but they actually dictate operating costs, risk exposure, and long-term performance. In other words: what flows through your pipes flows straight to your P&L.
Accurately designed pipelines ensure produced fluids get safely and economically transported to the next stage of processing or distribution, and the materials used, and the pipe material properties impact the three core areas:
- Types of fluid: What’s flowing (water, oil, chemicals, gas, steam).
- Service temperature: The temperature ranges the system must handle.
- Operating pressure: The pressure range during operation.
This article breaks down how pipe routing materials affect design and performance, compares common material options, and gives you a practical framework to help guide smarter decisions.
A Mini Case Study
A company sourced piping materials from Japan, selecting the right specification and brand, but opting for a lower-cost grade. They also selected intricate, highly nuanced designs (hoping for better control and sophistication), rather than opting for simpler, free-flowing options. Initially, the system ran smoothly. But within two months, cracks appeared, triggering a major gas leak, operational downtime, and serious safety hazards. In addition, the complex design with too many bends hindered flow, required more motor power, increased operating costs, and made repairs during the leak particularly challenging.
The short-term savings quickly vanished, as the organization had to replace the entire piping system.
The lesson? Cutting corners on material quality may seem economical at first, but it almost always leads to costly failures, operational headaches, and reputational damage sooner rather than later. Please note: Choosing an unnecessarily complicated design was also a contributor in this case.
Common Materials Used in Pipe Routing
When you hear “piping,” your first thought might be steel. But today’s routing systems can be built from a variety of materials:
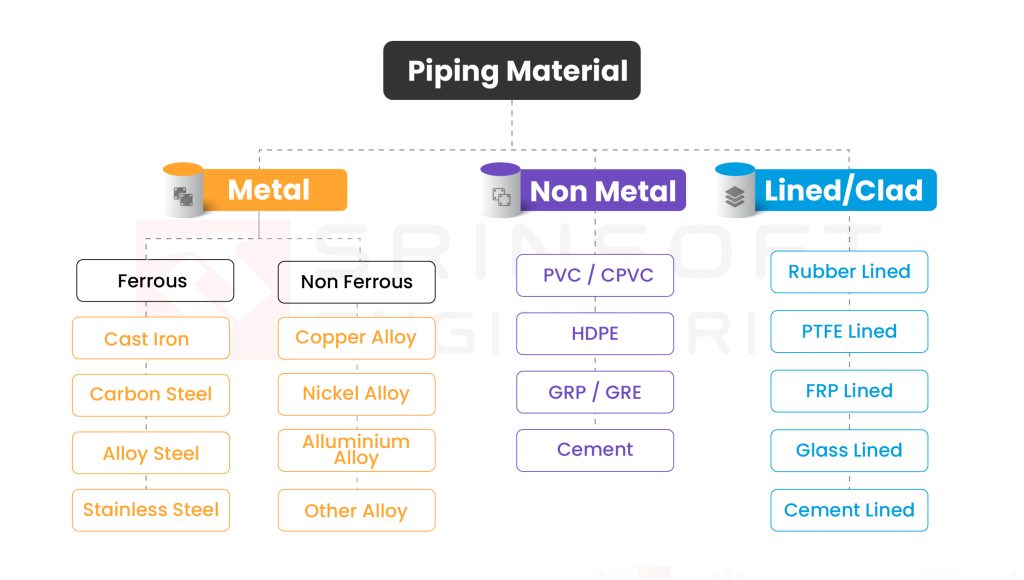
Let’s do a quick pipe material comparison across the dimensions (including PVC vs. Steel pipes) most executives care about— cost, durability, risk, and suitability for different conditions.
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | Low cost, lightweight, easy to install, corrosion-resistant Application: Residential, irrigation systems | May soften at high temperature/pressure |
| CPVC | Handles higher temps/chemicals, affordable, smooth inner surface resists debris buildup Application: Hot water distribution | Similar to PVC, but slightly more expensive |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, hygienic, high-strength, recyclable Application: Food processing, pharma, water purification plants. | Expensive, heavier, harder to install |
| Carbon Steel | High pressure tolerance, strong, versatile, and cost-effective over time Application: Oil and gas industry | Prone to corrosion unless coated, difficult to bend, and high maintenance |
| Copper | Excellent thermal conductivity, proven reliability Application: Medical applications, HVAC systems | Expensive, can corrode in acidic water |
| HDPE | Flexible, great for underground, chemical-resistant Application: Gas distribution, irrigation systems, sewer systems | Limited temperature tolerance, lower pressure, challenging bonding, and poor weathering |
How Material Choice Affects Routing Design
Your piping material selection defines not just the pipe, but the entire routing system’s performance and design.
1. Performance:
In a chemical plant, switching to high-performance alloys allows piping to carry hotter fluids at higher pressures.
2. Durability:
An offshore oil platform can use corrosion-resistant duplex steel, instead of standard carbon steel, to withstand saltwater exposure for decades without costly replacements.
3. Safety:
A food-processing facility can replace PVC with stainless steel to prevent chemical leaching.
4. Cost-Effectiveness:
A pharmaceutical company can invest in stainless steel instead of cheaper plastics to save millions over the system’s lifecycle.
How to Select the Right Material for Piping and Plumbing Design
Here’s a simple checklist to guide material selection decisions:
✅ Define the Operating Conditions
- What will flow through the pipe (water, chemicals, steam, gas)?
- What temperatures and pressures are expected?
✅ Assess the Environment
- Indoors, outdoors, underground, or exposed to corrosives/UV?
✅ Evaluate Lifecycle Costs
- Factor in not just purchase and installation but also maintenance, downtime risk, and replacement cycles.
✅ Match to Compliance Needs
- Does the system need FDA, USP, or sanitary compliance?
✅ Consider Installation and Routing Complexity
- Will lighter, flexible pipes reduce installation costs?
- Or do you need the strength and rigidity of steel?
✅ Run a Pipe Material Comparison
- PVC vs. Steel pipes, CPVC vs. Copper—compare side by side for your project conditions.
The right choice often comes down to trade-offs: spend more now to avoid risk later or save upfront with acceptance of ongoing maintenance costs.
Explore: Pipe Routing Codes and Standards
Emerging Trends in Pipe Materials
1. Smart Pipes and Sensors
The integration of sensors within pipes is like giving them a nervous system where a pipeline can now “feel” what is happening within it. Think of it as the pipe whispering to engineers about problems such as pressure building up, the temperature rising, or even the first hints of corrosion before they become disasters.
2. Nanotechnology-Enhanced Materials
Future pipes won’t just be metal tubes—they’ll be made with nanotech. Nanotech-enhanced materials are so tiny, you can’t even see them with a regular microscope. But they pack incredible strength; they are lighter, stronger, and nearly immune to rust and corrosion, and can better withstand demanding conditions such as harsh sea and acid flows.
3. 3D-Printed Pipes
Imagine printing a pipe the same way you’d print a photo—layer by layer, material stacked with precision. 3D printing lets engineers design pipes with twists, turns, and shapes that would normally be impossible. It can be printed on demand, with less waste and faster turnaround.
Vendor Selection – What to Look for in a Pipe Routing Partner
When it comes to material selection and pipe routing design, choosing the right vendor is just as critical as choosing the right materials. Here are five factors leaders should consider before signing on the dotted line:
Key Vendor Evaluation Criteria:
- Technical Expertise: Do they really have proven experience in BIM, deep MEP and piping design, and piping-specific coordination?
- Mechanical Automation Capability: Can they bring in automation tools to reduce errors, and is their documentation process future-proof?
- System Integration: Will their solutions integrate their design data smoothly with your ERP, PLM, or other enterprise systems so the design and installation are the same?
- Standards Compliance: Do they have experience and the ability to meet regional codes and industry standards anywhere in the world?
- Risk Reduction: Can they demonstrate a track record of minimizing failures, delays, and cost overruns, delivering accurate shop drawings and smooth handoffs?
Why It Matters?
- Material failures cascade into operational disasters caused by wrong material impact on routing.
- Wrong material choices lock you into decades of higher maintenance costs.
- Regulatory compliance depends on material specifications, making poor choices a direct path to legal liability.
- Your material decisions today determine whether your infrastructure can adapt to future operational changes.
- Insurance premiums and operational permits are directly tied to material quality, affecting profitability beyond initial investment.
Conclusion
Choosing the right material is not just a small detail in the design plan. It’s a strategic decision that involves defining operating conditions, fluid characteristics, chemical compatibility, mechanical stress, application-specific requirements, and compliance and standards.
Here’s the bottom line: every pipe material decision shapes performance, efficiency, and resilience. Get it right, and you unlock reliability and savings. Get it wrong, and the hidden risks can turn into expensive, headline-making failures.
Material selection is yours. Ensuring those choices integrate flawlessly into BIM, design, and automation—that’s SrinSoft. Reach out to the SrinSoft experts today and elevate your engineering outcomes!