
No race is won in the first corner, but many are lost there.
In pipe routing, the first corner is designed to follow industry codes and standards. They form the foundation that protects your investments and operational integrity. Skip them, and the result isn’t just a technical flaw, it’s watching carefully planned ROI vanish like a soap bubble.
Pipes are the unsung heroes of modern industry, quietly transporting everything from petrochemicals to pharmaceuticals; without them, nothing “flows.” Think of them as the corporate IT team: nobody notices them when they work, but when something breaks, suddenly everyone’s paying attention.
Pipe routing can raise many questions, such as whether a pump should have designated connection points or if an open hole of a specific size provides enough information for the fitting to attach, just to name a few.
In this blog post, as the title suggests, we will discuss pipe routing and the role that codes and standards play in protecting your ROI.
What Is a Piping Code?
A piping code is a set of general rules or systemic standards for the design, fabrication, installation, inspection, and testing of piping systems. Codes serve as the legal framework — they can be adopted by a legal jurisdiction and made into law — and a technical framework ensuring that piping systems operate safely under defined conditions.
For example:
- ASME B31.1 (Power Piping) covers systems in electric power plants and district heating.
- ASME B31.3 (Process Piping) defines requirements for chemical plants, refineries, and other process industries.
Codes dictate what must be done to prevent catastrophic failures such as loss of life and property, plant shutdowns, and resultant financial loss. Revisions to these codes are published periodically, and professionals must be refreshed on the latest editions, addenda, and revisions affecting their line of work.
Would you trust a billion-dollar facility to piping systems designed without the very standards meant to protect it?
What Is a Piping Standard?
A piping standard is like the recipe book of the piping world, it lays out the right dimensions, materials, and best practices so everything fits and works together. Unlike codes, standards aren’t always mandatory, but most engineers and engineering design service providers follow them anyway to streamline design, procurement, and maintenance.
For example:
- ANSI pipe standards are like a tape measure; they specify pipe dimensions, flanges, and fittings so nothing is left to guessing and rework.
- ISO standards promote international uniformity in materials and testing procedures; they ensure, for example, a valve ordered in Houston actually fits a pipe designed in Hamburg.
In short, standards are about how things are done. They reduce project risks and supply chain complexity.
Understanding Piping Codes vs. Standards
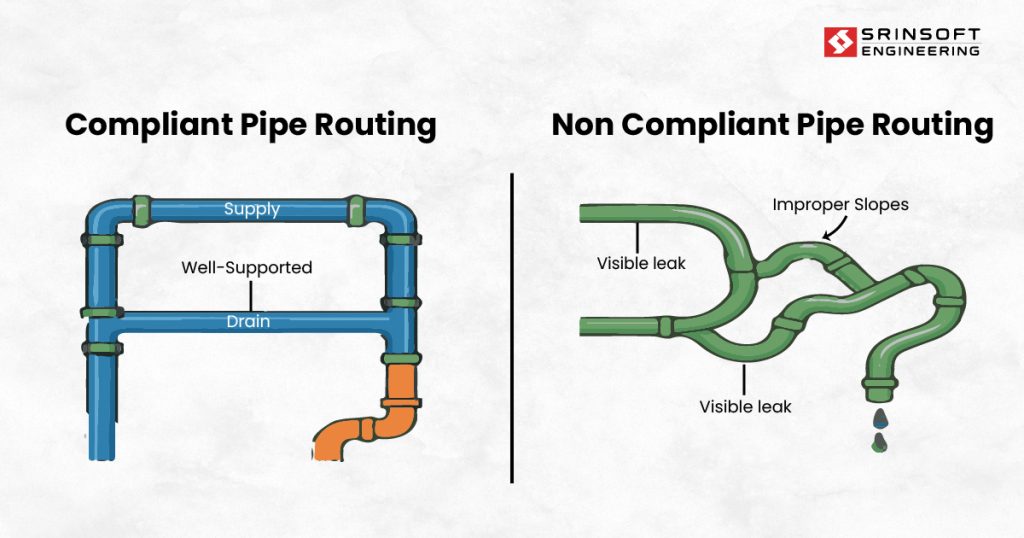
It’s easy to confuse codes and standards, but their roles are distinct:
| Aspect | Codes (e.g., ASME B31.3) | Standards (e.g., ANSI, ISO) |
| Purpose | Ensure safety and legal compliance | Ensure consistency and interoperability |
| Mandatory? | Yes, often legally enforced | Not always, but widely adopted |
| Scope | Design, fabrication, inspection, testing | Materials, dimensions, practices |
| Example | ASME B31.3 for process piping | ANSI pipe dimension standards |
In practice, both work hand-in-hand, codes set the safety rules, while standards are the detailed instructions. Think of it as the CEO setting the strategy and the COO making sure the day-to-day actually works.
How Codes Influence Routing Design
Piping compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes, it’s the rulebook that decides whether your system runs smoothly or turns into an expensive game of ‘guess that leak.’ Codes and standards shape every design decision, including:
1. Pipe Spacing and Layout
A pharmaceutical company fast-tracks a cleanroom expansion but ignores spacing standards. Pipes are crammed too close together. Six months later, a small leak requires repair—but maintenance crews can’t access the faulty section without dismantling half the line.
2. Slope and Drainage
A beverage manufacturer installs pipes without proper slope compliance. Water and syrup residues settle in low points. Over time, bacteria build up, forcing a full-scale product recall when contamination is discovered.
3. Flexibility and Thermal Expansion
An oil & gas facility skips expansion loops to save on steel. In peak summer, thermal stress warps the lines, causing cracks. The plant must shut down, losing weeks of production during a high-demand season.
4. Supports and Restraints
A new data center cooling system is built with undersized supports to cut costs. When high-pressure pumps kick in, vibration loosens the lines. The result? A sudden coolant leak near critical servers.
5. Stress Analysis
A chemical plant skips rigorous stress analysis to save design hours. Months into operation, uncalculated forces cause a joint failure. A minor chemical release triggers an evacuation and OSHA investigation.
Risks of Ignoring Piping Standards
If compliance failures can shut down production, trigger fines, and damage brand reputation, can you really afford to treat standards as optional?

Cutting corners in pipe routing is a gamble executives can’t afford. The risks extend beyond engineering to strategic and financial domains:
- Safety Hazards: Imagine a food processing plant where low-grade piping was installed to cut costs. Months later, a minor leak releases ammonia gas.
- Regulatory Penalties: A refinery expansion project bypasses ASME B31.3 guidelines to speed up commissioning. During a surprise inspection, regulators discover non-compliant welds. The plant faces hefty fines, delayed startup approvals, and must redo critical sections. The project slips by six months . a direct hit to revenue forecasts.
- Operational Downtime: At a pharmaceutical facility, non-standard pipe routing creates hidden stress points. A pipe bursts in the sterile area, halting production.
- Reputation Damage: An energy company rushes a project with non-compliant piping to showcase its “agility.” Later, a leak causes an environmental incident. Headlines name the company as “cutting corners,” and investors demand accountability.
- Escalating Costs: A new chemical plant saves 5% upfront by using lower-standard fittings. Two years in, corrosion forces major retrofitting. Production is offline for weeks, contractors must re-engineer sections, and litigation looms with clients waiting on delayed deliveries.
Conclusion
The compliance decision you make today determines whether your project delivers planned ROI or becomes a cautionary tale.
Every day, executives face a choice: invest in proper pipe routing compliance upfront, or gamble with retrofits, penalties, and reputation damage later. The math is simple, compliance costs pennies on the dollar compared to failure.
Your competitors are making this decision too. The smart money follows the standards.
Executive Summary – Why It Matters
- Compliance protects ROI, safety, and reputation.
- Non-compliance leads to costly risks and downtime.
- Strategic adherence turns pipe routing into a business advantage.
Why SrinSoft
- SrinSoft Engineering Coordinate 3D Piping Models & Shop Drawings
- MEP BIM Services tailored for compliance
- Automation Capabilities that streamline design workflows, documentation, and QA.
Don’t Let Compliance Failures Derail Your Next Project
Every day of delay costs your project. Every compliance failure multiplies that cost exponentially. Our 20+ years of compliance expertise means your piping systems are designed right the first time, on schedule and on budget.
**Schedule a 30-minute risk assessment call** where we’ll review your current project timeline and identify potential compliance bottlenecks before they become expensive problems.


